As we settle into our new home, I’ve been busy reading and learning all I can about Québec City and its history. Honestly, I’ve become a little obsessed because there are just so many interesting stories and details, which I’m very excited to share. And since I learned a lot of this information through various walking tours, I decided to organize this into a sort of virtual walking tour for anyone to enjoy! On y va!
Stop 1: Parc des Gouverneurs

I want to start our little tour at the Parc des Gouverneurs, which sits right next to the famous Château Frontenac and has a beautiful view of the Saint Lawrence River. I think this is a great place to begin because from here you can see both sides of the river and Île d’Olréans, which is the official start of one of the largest estuaries in the world. An estuary is where a river turns into an ocean, and this particular narrowing is precisely why Québec City is where it is, and it’s also how the city (and the province) got its name. Québec means “where the river narrows” in Algonquin.

Partly due to its location, Québec City has played an important role in the history of North America. Founded in 1608, it was the first permanent settlement of what was then New France, and like many of Canada’s first cities, it started as a trading center. However, its strategic position and striking natural features are what prompted early explorers and settlers (first Cartier and then Champlain) to develop the area. Cartier couldn’t quite handle the harsh winters here, so he came and went a few times, but it was Samuel de Champlain who decided to buckle down and make Québec City a home.
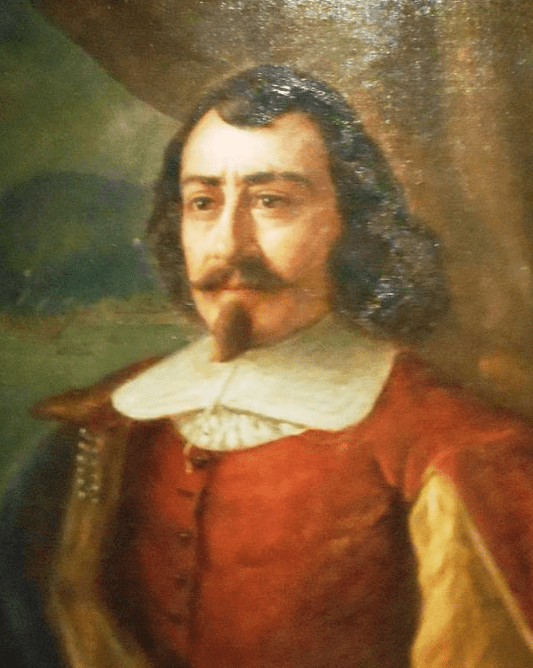

Along with a small group of initial settlers, Champlain built the first habitation in Québec and quickly became known as the Father of New France, which is why his face is everywhere around the city. Well, not his face exactly. Apparently, Champlain never actually had a portrait done, so we don’t know what he looked like, and when the city started putting up statues of him, they had to just go with another noble-looking French guy instead. So, in all the artwork, statues, and history books, the man you’re looking at is not Champlain, but at least they stayed consistent with the image.
Stop 2: École des Ursulines
Our next stop is the École des Ursulines, which began as a monastery that was founded in 1639, making it the oldest educational institution for women in North America. One of the founders was Marie Guyart (aka Marie de I’Incarnation), a French widow turned nun, who came to Québec to educate young girls in the new colony. Because she had been married before and still had a son in France, she wrote thousands of letters about daily life in New France, the indigenous people of the region, and many other events that historians are still pouring over. For her contributions, she has been memorialized across the city and beyond.


Québec City (and all of its early inhabitants) really saw a lot of important events unfold in what was a fairly turbulent time for North America. Québec City sits on a 300ft cape situated at the narrowest point of a difficult-to-navigate river, meaning it was pretty intimidating even before all the fortifications, which is likely why there have only been a handful of battles fought here. The first battle is one of the most famous (and interesting) because it was won with a bit of psychological warfare. Louis de Baude de Frontenac, the Governor General at the time (1690), gave the iconic “I’ll answer the with the mouths of my cannons” line after blind-folding and tricking a scout into thinking Québec was much more battle-ready than it actually was.

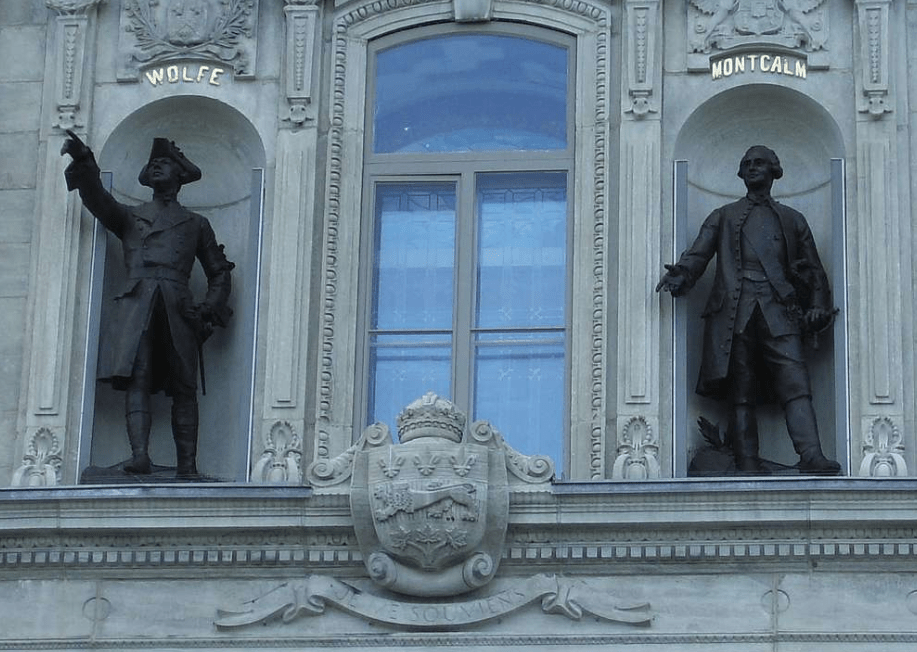
Another famous battle took place here in 1759: the Battle of the Plains of Abraham, which is essentially how the British ended up with all of Canada. Interestingly, although the British won the battle, the generals on both sides, Wolfe (EN) and Montcalm (FR) are still well-represented throughout the city. Also, of interest is the fact that Montcalm’s remains were actually found beneath the floors of the École des Ursulines somewhat recently (2001) because one of the nuns ended up sharing that little piece of history on her deathbed. What a way to go out!
Stop 3: St-Louis Gate

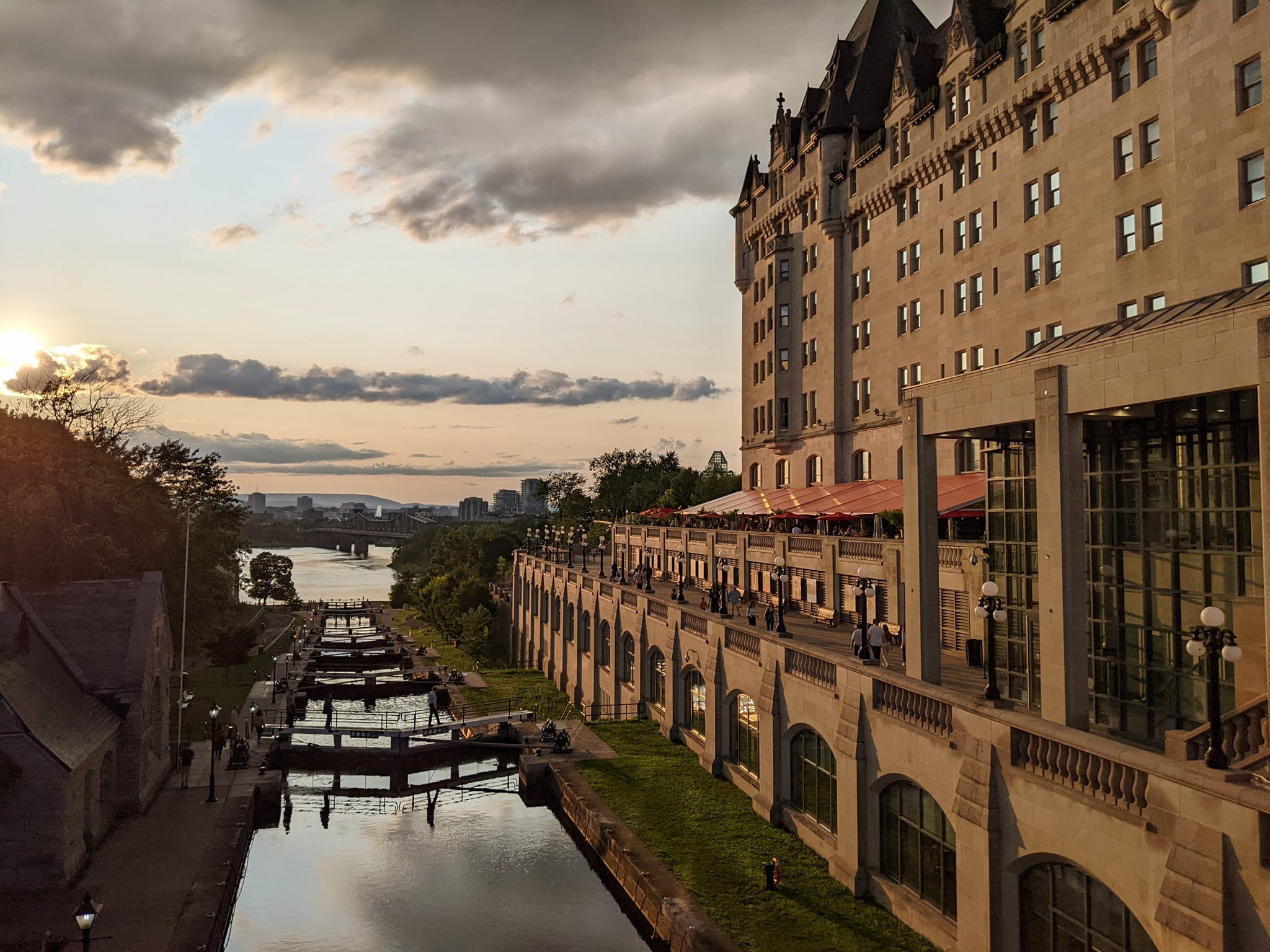
Next, we’ll take a stroll over to the St-Louis Gate, one of the oldest gates in the city. The St-Louis Gate stretches over rue St-Louis, which was one of the first roads in Québec City as it led directly to Fort St-Louis, Champlain’s (and later several other Québec leaders’) official residence. The fortifications around all the city gates weren’t actually completed until a bit later, and the city wasn’t 100% walled-in until after 1820 when British troops finished the job. It was quite a job, too, because the walls stretch over 4.6kms (2.9mi). At one point, there were over 300 cannons lining the walls, which definitely added to Québec’s image as a hard-to-conquer city.
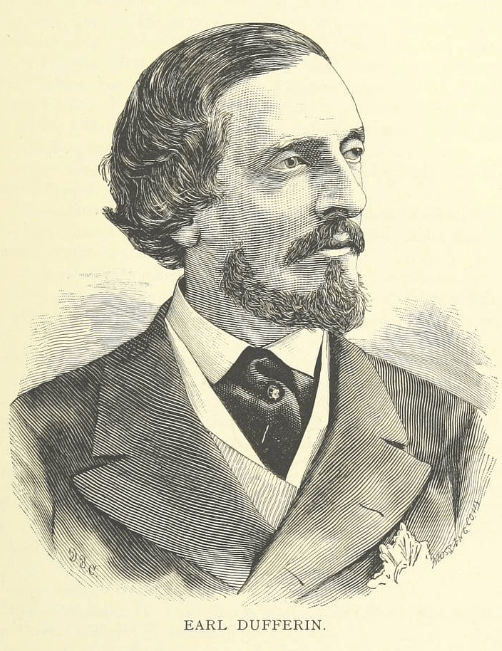

Of course, eventually, the wars ended and things settled down in North America, and Quebecers had to decide what they wanted to do with their fort of a city. Many wanted to tear down the walls and start over with more of an open-concept. However, another Governor General, Lord Dufferin, had a different idea. He had traveled extensively and knew that Québec’s walls were an architectural jewel that needed to be preserved, and thankfully, he was able to persuade everyone else. By preserving the fortifications, enlarging the city gates, and building a massive public boardwalk, Lord Dufferin ensured Québec City would be welcoming tourists long after he was gone.
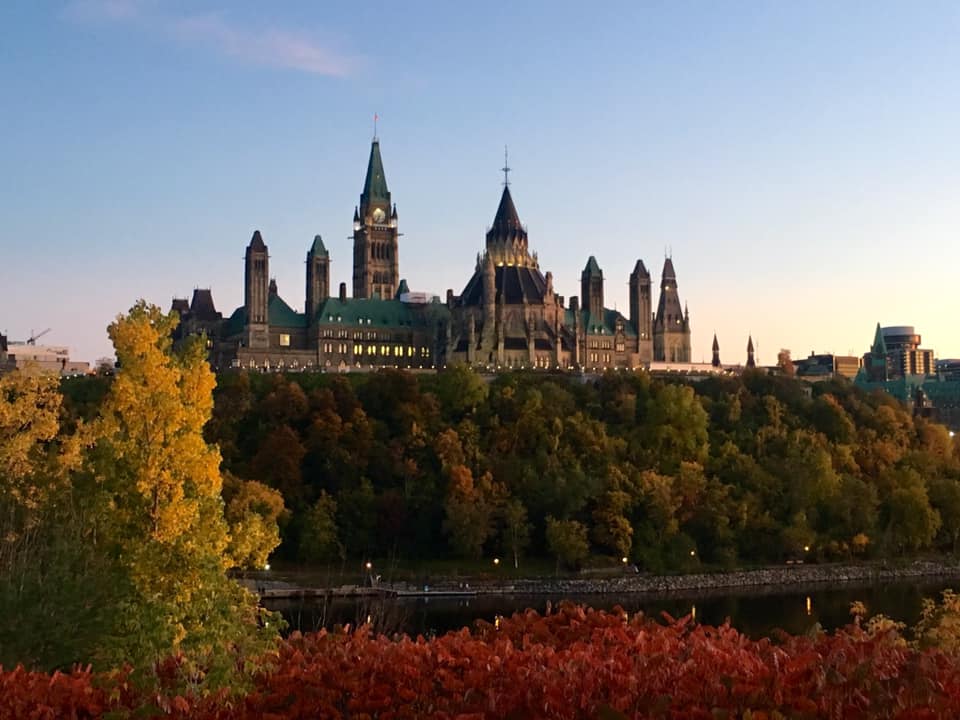
The city’s infamous walls encircle what is now known as Vieux Québec (Old Québec), and in 1985, this section of the city became a UNESCO World Heritage site, meaning it’s now protected by international law. Lord Dufferin would be happy. However, life goes on and cities grow; therefore, there are a lot of important places outside the walls now too, including the Parliament Building of Québec, which was built in the late 1800s and was inspired by the Louvre – a somewhat obvious nod to France as opposed to Britain. Old habits die hard it seems.

Stop 4: Overlook at St-Jean
Another important part of the city that technically lies outside the fortifications is Basse-Ville (or Lowertown). This part of the city is important for many reasons, one of which is the fact that I live here. 😊 But I’m not the only one! La Basse-Ville was, historically, where the average Quebecers lived, the working-class people, and Haute-Ville (or Uppertown), which includes Vieux Québec, was where the upper classes lived: governors, doctors, lawyers, etc. Funny how it still sort of works like that, non? I can attest Basse-Ville is definitely cheaper than Haute-Ville.


And nothing makes me feel the socio-economical difference more than when I have to make the trek up to Vieux Québec. Cape Diamant was great for battles and enemy intimidation, but it’s definitely tough on the knees! There are approximately 30 staircases throughout the city connecting Basse-Ville to Haute-Ville. Our closest staircase is Lépine, which has 118 stairs going straight up the cliff. Perhaps the most famous staircase though would be Casse-Cou (or “Breakneck”). It’s located in the oldest part of Basse-Ville, and has a bit of a rough history. The stairs, much like the neighborhood itself, were often in disrepair and led to many accidents, thus the name.
Interestingly, you’ll see a lot of buildings high-up on the cape, but you won’t see so many skyscrapers in general in Québec City. That’s because the two tall buildings that were built in the Old Town really ticked off the locals at the time, forcing them to enact a law banning any buildings over 7 stories tall. The two buildings in question were allowed to stay, however. One is the Price Building (1929) which was originally a lumber firm’s headquarters, but now houses the Premier of Québec, and the other is an addition to Hôtel-Dieu de Québec (a teaching hospital), which obviously had good intentions, but was really quite ugly.
Stop 5: Morrin Centre

Now onto a few buildings that are anything but ugly, starting with the Morrin Centre. This building has quite a varied history and is so well-hidden in the heart of the city that I might never have known about it if not for the walking tours. It was originally the city’s prison, and despite its stately appearance, you can still pretty easily see where the bars were attached to the windows. Unfortunately, it wasn’t long before the city needed a larger prison (which was built on the Plains of Abraham and is now an art gallery), so the Morrin Centre became an English college. Today, it still functions as an English library and cultural center that has fun events like Victorian-style teatimes and summer reading clubs.

Right next to the Morrin Centre/English library is an old church turned French library, Maison de la Littérature. I absolutely love the relationship between English and French here in Canada, but particularly in Québec, it never ceases to amaze me! Early on in my studies of Canadian history I wondered how Québec remained so French given the fact that the English took over in the 1700s. Surprisingly, it’s because of the US. The British during that time were so afraid the French would swap sides and join the Americans that they signed the Québec Act ensuring Québec could keep their language and local laws as long as they wouldn’t fight against them. Well, they never did and have kept their French-ness ever since.

The Morrin Centre and Maison de la Littérature are great examples of something Québec City has done amazingly well time and time again: historical site conversion. It seems there’s not a building around that doesn’t have an extensive and diverse history, which is why I keep reading every sign and every plaque I come across. There’s a museum that used to be the old city vault, a private club that was once a military barracks, and pretty much every restaurant downtown was someone’s house at some point. 400+ years is a long time for social institutions, but not so long for buildings.
Stop 6: Notre-Dame
Next stop: church. La Notre-Dame de Québec to be exact. While not technically the oldest church in the city (we’ll get there soon), Notre-Dame de Québec has its fair share of interesting stories and facts as well. First, it has burned down and been rebuilt three times since its original 1647 construction date, which is pretty impressive in and of itself. You might also notice that there’s only one completed bell tower giving the church a unique, asymmetrical look. Well, that was actually due to a miscalculation on the architect’s part, which resulted in it being deemed unsafe to finish. Oopsies!
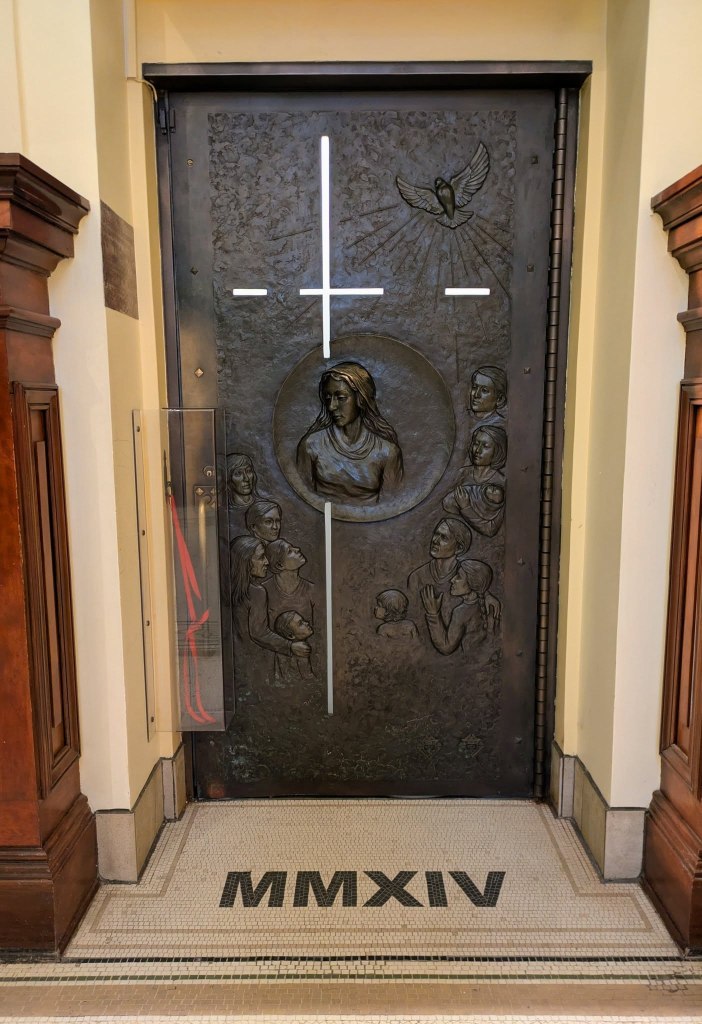


And while it might not have all its intended bell towers, it does have something super rare: a Holy Door. There are only a handful of Holy Doors in the world, the vast majority of which being in Italy, so this one (the only one in the Americas) is quite special. What is a Holy Door you ask? Well, I’m not quite sure. It’s only opened on jubilees, so I’ll have to wait a number of years for the chance to walk through it and experience its power myself. What I can say is that, currently, it’s sealed very much like the Pope’s door during the Conclave, which is still pretty cool to see.

While we’re on the topic of the city’s religious history, we should also take a look at the Séminaire de Québec, which is right next door to Notre-Dame. The Seminary of Québec is often touted as the oldest educational institution in Canada, and its buildings still house several schools today, including many departments of L’Université de Laval, the first French-language university in North America and the oldest university in Canada. You’ll see and hear the name Laval quite often in Québec because he was New France’s first bishop.
Stop 7: Château Frontenac

It’s finally time for the structure that dominates pretty much any photo of Québec City, Le Château Frontenac! Earlier, I mentioned Fort St-Louis as one of the first buildings in the city (aka Champlain’s home). Well, the Château Frontenac and Lord Dufferin’s boardwalk are actually sitting on top of the ruins of Fort St-Louis. In fact, you can see quite a bit of them on display beneath the boardwalk. Also, on the boardwalk is a massive statue of Champlain (but not his face, remember). Two other interesting facts about this statue: one, it was actually designed by an architect who survived the Titanic, and two, the base is made of the same stone as that of the Arc de Triomphe – connections to France abound!
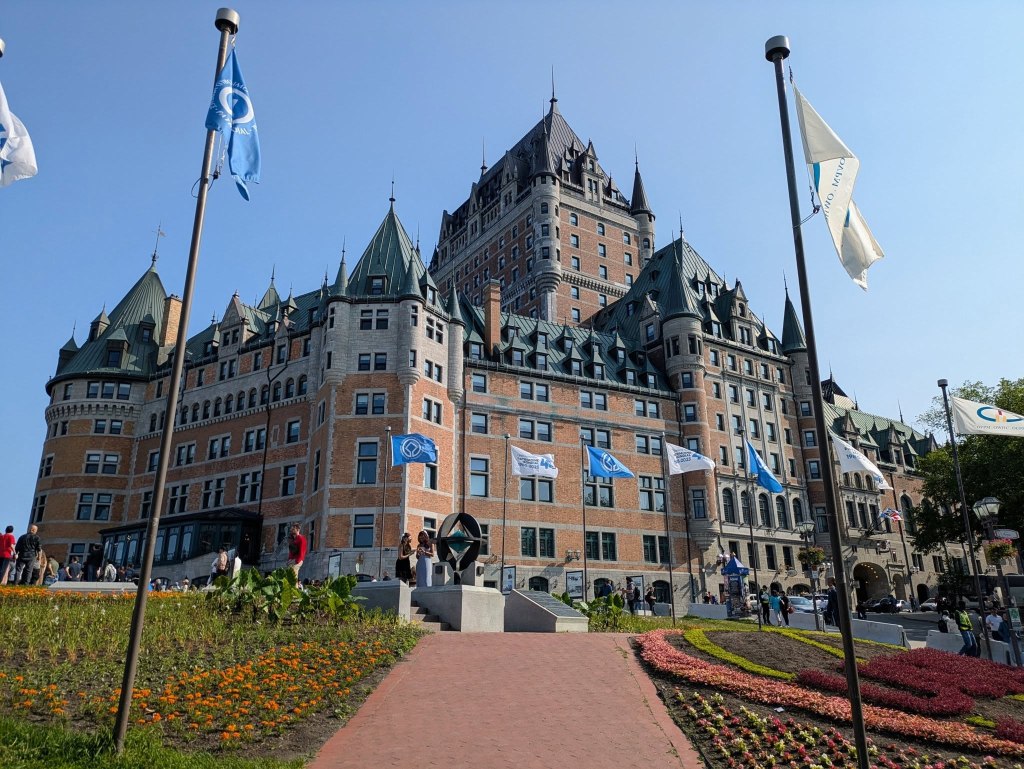

The Château Frontenac itself wasn’t built until 1893, and despite the name, it isn’t actually a castle. It was built as a hotel, and that’s what it’s always been. Like the Château Laurier in Ottawa, it’s one of the Pacific Railway Hotels, which are all incredible pieces of architecture spread across the whole of Canada. Another interesting fact about the Château Frontenac is that the main tower, arguably its most distinguishing feature, was an afterthought, added in 1924. The hotel has actually had a lot of work done over the years, including the addition of a pool and fitness center, which was done solely to maintain its coveted 5-Star status.
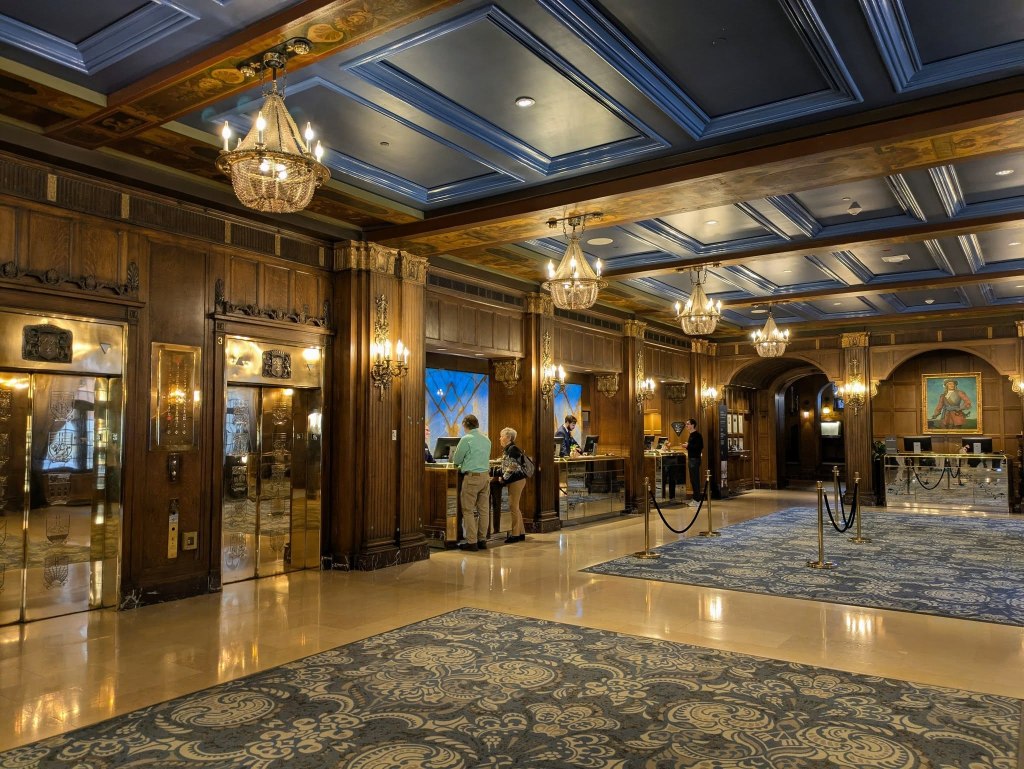

As you can imagine, many famous people have graced the halls of this amazing building: Queen Elizabeth, Winston Churchill, FDR, Princess Grace of Monaco, Charlie Chaplin, Céline Dion, Paul McCartney, and Leonardo DiCaprio, just to name a few. There are 610 rooms/suites in the hotel, and thanks to some progressively-minded designers, there is no hierarchy to the placement of the various rooms and suites. You could book their cheapest room and end up on the top floor with a view of the St-Lawrence. Of course, even the cheapest room is still around $300, but still.
Stop 8: Montmorency Park

Walking down one of the many staircases in the city, we cross Prescott Gate and come to a stop in Montmorency Park. Now a beautiful park somewhat between Basse-Ville and Haute-Ville, Montmorency was first a farm. Actually, the first farm in New France, created by two of the early settlers: Louis Hébert and Marie Rollet. They were one of the first pioneer families in Canada and have come to represent a lot of the early values of the region: perseverance, adaptability, amity, etc. Across from the park, you can see (and smell) Mary’s popcorn, which I think is a lovely connection between the region’s entrepreneurs, both past and present.
As the farm gave way to modern building projects, Montmorency later became the site of the first parliament buildings of Québec and later Lower Canada. In 1864, the British North America Act, a founding document of modern-day Canada, was actually drafted there. Unfortunately, a fire destroyed the last of the buildings in 1883, which is when the city decided to move Parliament outside the Old Town (for safety reasons, of course).

From Montmorency Park, you can also see the Casse-Cou stairs, which take you down into Quartier Petit-Champlain. This is the neighborhood I mentioned earlier that has a bit of a rough history. Basse-Ville was where the working class lived, and so there was never a lot of money there. But there has always been an entrepreneurial spirit! Petit-Champlain is often sited as the continent’s first commercial district, and when you look down its bustling streets lined with business after business, that’s really easy to believe.
Stop 9: Place Royale
But the heart of Basse-Ville has to be Place Royale (or Royal Plaza). This was where the first settlers stepped off the boat and began their lives as a new colony. The first permanent buildings were built on this square along with the first church of Basse-Ville (technically the oldest church in the city since it still has its original walls). You can still see the foundation stones for the second habitation among the cobblestones of the square. Also in the square, stands a bust of King Louis XIV, and although it isn’t the same bust from the 1600s, there has almost always been a bust in that exact spot, forever linking the histories of Québec and France.
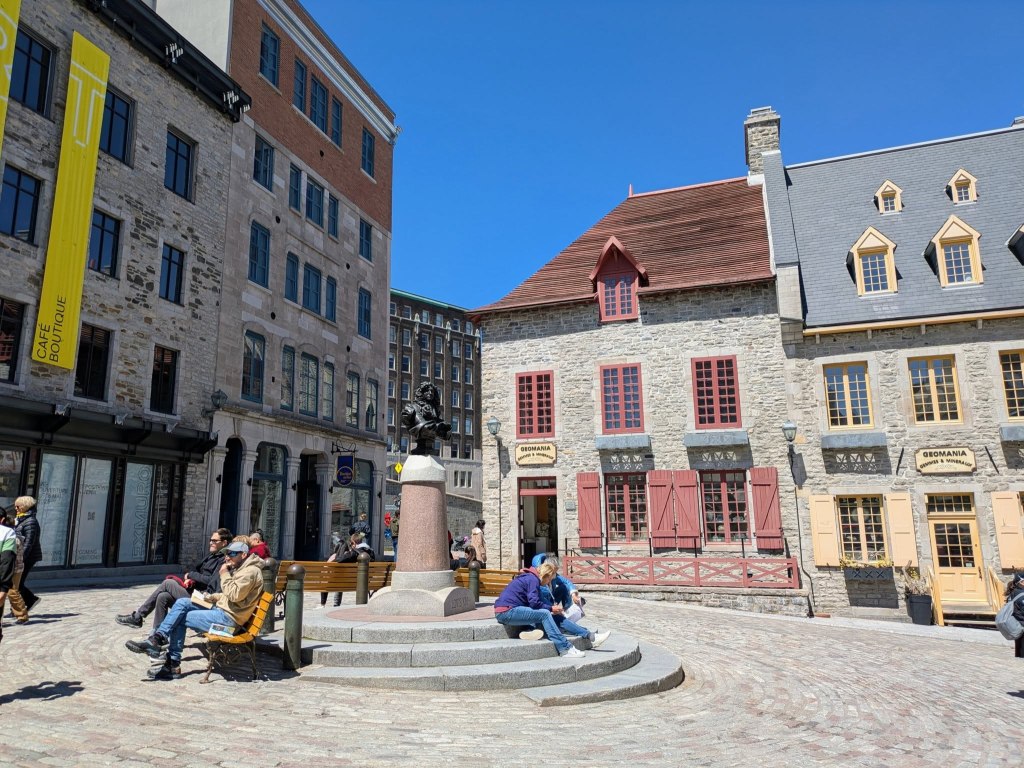

Interestingly, the king never actually stepped foot in Québec even though he was the lawful ruler, but he did manage to help the colony from afar. In the early days, the colony struggled with population issues. In particular, not enough women were there to ensure the desired population growth, so King Louis started a program where he would give a dowry and land to any females willing to journey to New France and start a family. Usually, these were orphans or widows who felt that this was their best option for a stable future, and so they became known as the King’s Daughters.

The King’s Daughters made up such a large percentage of the early population in Québec that many North American celebrities have been able to trace their lineage back to one of the daughters: Hilary Clinton, Madonna, Angelina Jolie, and Tom Bergeron being among them. Honestly, Québec City has a lot of ties to various celebrities. Since the city basically looks like a movie set and also has the practical, money-saving advantage of being on the same continent as Hollywood, many movies that take place in Europe are actually filmed here. Alfred Hitchcock’s “I Confess!” and Steven Spielberg’s “Catch Me If You Can”, for example.
Stop 10: Royal Battery

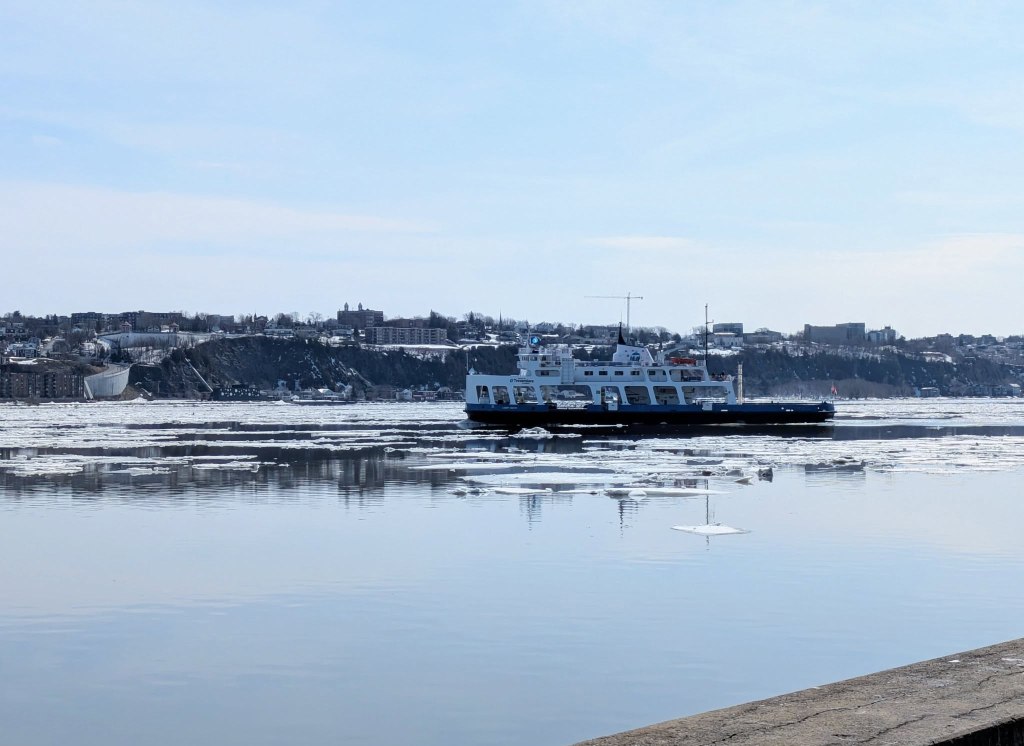
And now we’ve come to the last stop on this (maybe not-so-little) tour. The Royal Battery is the end of the line so to say. It’s where the city meets the river. Here you can see the ferry that travels across the St-Lawrence to Lévis, the often-forgotten little brother of Québec City. You can also find fishing expeditions or whale watching tours departing from these quays; this is where the river turns to ocean after all. When there’s no ice in the water, you might also see cruise ships and yachts docking at the Old Port, which I like to imagine is just as exciting as when Champlain and other early explorers rolled up in their ships.
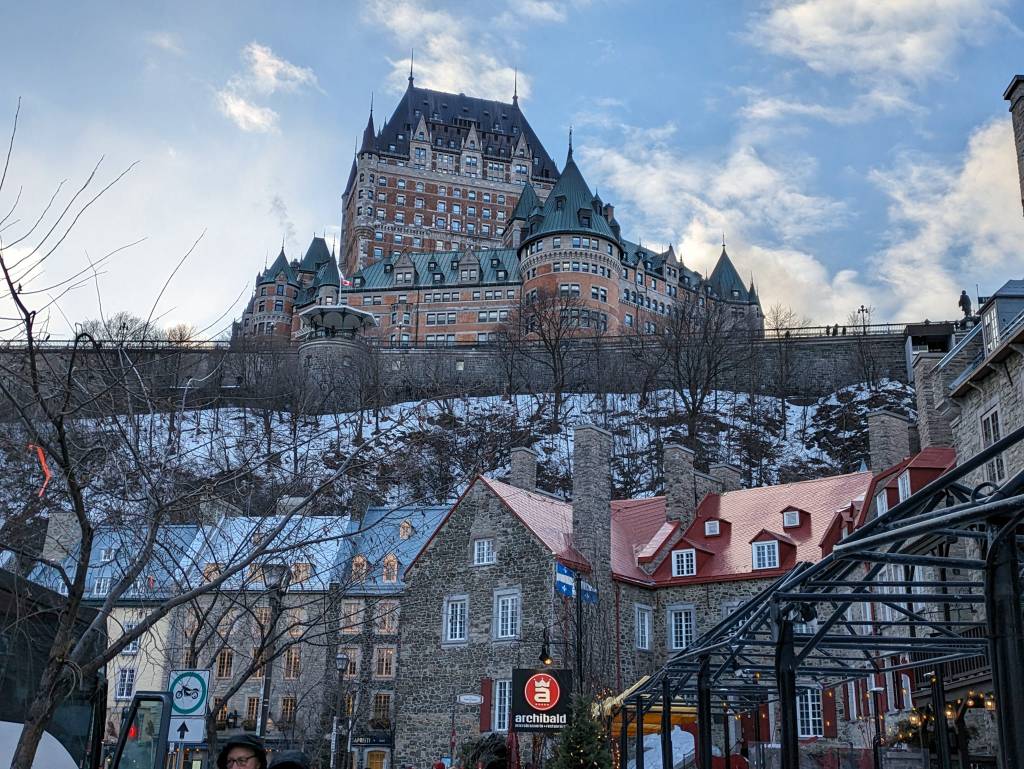

From the Royal Battery, it’s easy to imagine how tough it would have been to take Québec City by sea. The British only managed a win because they fought on the Plains of Abraham (flat ground beyond the walls of the city). During the American Revolutionary War, Generals Benedict Arnold and Richard Montgomery thought they’d give it a shot, but it went very badly for them, and no one has tried since. Thus, Québec City gets to keep its impressive win/loss record.
Near the battery, you’ll also find the funicular, which leads back up to Haute-Ville, where we started this adventure. The funicular entrance is located in a house that dates back to 1682 and used to belong to Louis Jolliet, another famous North American explorer you might have heard of. Really everywhere you look in Québec City there’s another piece of the gigantic puzzle that is our history just waiting to fit into place. One of Québec City’s nicknames is The Old Capital, but I see it more as an entryway. Here you can enter North America, but you can also enter the annals of history. Hope you enjoyed the journey!